Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on how a person’s thinking affects their feelings and behaviors.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on how a person’s thinking interacts with their feelings and behaviors. This approach is based on the idea that a person’s symptoms can be maintained or intensified by their patterns of thought. CBT is one of the most commonly used forms of therapy, and there is a significant amount of research evidence pointing to its effectiveness.
What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness’ definition, cognitive behavioral therapy, “focuses on examining the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.”
There are several types of CBT, but many share a few common elements. Most forms of CBT are:
Treatment Can Be Life Changing. Reach out today.

- Brief and time-limited due
- Present centered
- Thought focused
- Guided by practice and homework
- Based on a strong therapeutic relationship
In most scenarios, CBT can be broken down into two components: functional analysis and skills training. The initial phase, functional analysis, includes identifying high-risk situations that may trigger the patient to experience difficulties. After a patient has developed insight regarding their thoughts, CBT typically shifts to the phase of skills training. This phase focuses on reducing reliance on old, unhelpful habits and learning new, healthier ways of framing one’s life experiences. The specifics of each phase will differ greatly between each patient and their counselor, as the approach is able to be highly individualized.
History of CBT
Cognitive-behavioral therapy emerged at a time when the field of psychology was dominated by Freudian psychoanalysis. In the early years of the history of CBT, the approach rebelled against the former gold-standard techniques and focused on reducing problematic behaviors through scientifically based strategies. As time progressed, the approach grew to include a greater focus on thoughts rather than strictly problematic behaviors. The study of human thought and behavior led pioneers of CBT to identify the cyclical relationship between a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Types of CBT
In most situations, CBT will have some of the same basic elements. However, there are several different types of CBT, each with a slightly different focus or approach, including:
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT): Focuses specifically on the resolution of emotional and behavioral problems through changing irrational beliefs to more rational ones.
- Cognitive Therapy: Has been used most commonly for depression. Cognitive therapy is focused on recognizing negative thought patterns and inaccurate beliefs.
- Multimodal Therapy (MMT): Incorporates techniques to address symptoms affecting seven interrelated dimensions or modalities of human functioning. MMT is eclectic in the techniques used but theoretically remains consistently based in CBT.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Focuses on emotional regulation, building distress tolerance and increasing effective interpersonal skills. Mindfulness skills are incorporated throughout DBT as a compliment to the CBT-based therapies.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Based on the acceptance of negative or unpleasant emotions to avoid overreactions. Behavior change strategies are used to increase flexibility in one’s thinking.
- Trauma-Focused CBT: Primarily focused on treating the distinct needs of individuals who have experienced trauma. Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy is most commonly used with adolescents and their families.
Goals of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
The main goal of cognitive behavioral therapy is to identify and change inaccurate and unhelpful beliefs and thought patterns. To achieve this goal, therapy will typically have several smaller, more specific goals.
Other common goals of CBT providers include:
- Teaching patients to recognize faulty thinking patterns which create problems and reconsider these thoughts from a more realistic perspective
- Assist patients in developing a better understanding of both their own behaviors and motivations and those of others
- Guide patients in applying problem-solving skills to cope with difficult situations
- Coach patients as they develop a greater sense of self-confidence and self-actualization
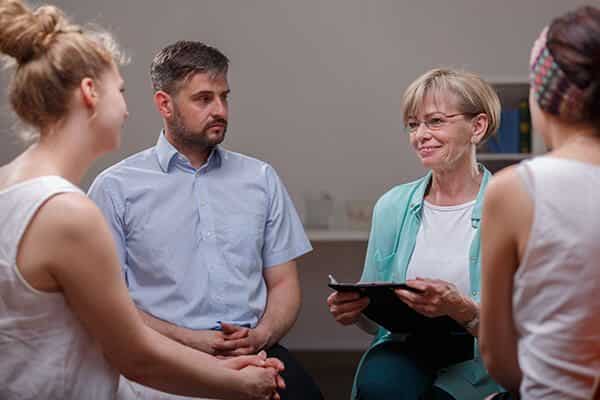

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques
There are many specific cognitive behavioral therapy techniques commonly used by most counselors practicing this approach. However, the cognitive-behavioral therapy exercises which are ultimately implemented depend on an individual’s treatment plan and their presenting problems. Some examples of cognitive behavioral therapy techniques include:
- Identifying and challenging negative beliefs and patterns of thought
- Mindfulness-based exercises which encourage focusing on the present moment and accepting feelings and thoughts
- Relaxation techniques, such as visualization and deep breathing exercises
- Implementing problem-solving models
- Roleplaying potentially distressing situations
- Homework assignments between sessions to help practice new skills
- Social, communication or assertiveness skills training
CBT Treatment
Researchers have found that CBT is helpful for a vast array of conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, personality disorders and substance use disorders, among others. In some cases of cognitive behavioral therapy for depression, this approach has been demonstrated to be as helpful as antidepressant medication. When CBT is used for depression, patients may be encouraged to increase participation in pleasurable activities, improve basic self-care habits and restructure negative thinking patterns.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxiety is another common application of this approach. Often, patients who experience anxiety will be led through the process of testing out beliefs that may contribute to their anxiety. Through this process, the frequency and intensity of bouts of anxiety are improved. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for addiction has gained increased supporting evidence. A person receiving this type of treatment for a substance use disorder will often develop insight regarding their triggers while working to develop relapse prevention skills. These are just a few of the applications of CBT.
CBT can be used to treat many mental health conditions, including:
- Depression
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Social anxiety
- Specific phobias
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Bipolar disorder
- Binge eating disorder
- Bulimia
- Anorexia
- Body dysmorphic disorder
- Dissociative disorders
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
CBT can also be used to address substance use disorder and related concerns, including:
- General relapse prevention skills
- Withdrawal
- Smoking cessation
- Gambling addiction
- Marijuana use disorder
- Alcohol use disorder
- Cocaine use disorder
- Amphetamine use disorder
- Opioid use disorder
- Other substance use disorders
CBT may be used to treat more than one condition at a time. For example, one study found that patients receiving CBT for both substance use and depression had overall positive outcomes. Another study made similar conclusions, though additional research is needed to demonstrate the level of effectiveness of CBT for co-occurring disorders.
CBT can also benefit non-clinical conditions, such as:
- Medically related disorders
- Criminal behaviors
- General stress
- Chronic pain
- Insomnia
Effectiveness of CBT
The effectiveness of CBT has been so well demonstrated that it has been called the gold standard of therapy. There are several reasons for this designation, including the fact that CBT is currently the most researched therapeutic approach. When two or more therapeutic approaches have been compared by researchers, CBT is typically found to be more favorable. No other approach has been found to be more effective. In some cases, CBT has been found to be more effective than medication in treating mental health conditions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Near Me
To find cognitive-behavioral therapy near you, you may wish to start by speaking with your primary care physician. A treatment locator tool may also be helpful in locating a licensed cognitive behavioral therapy practitioner near you. The Recovery Village Palm Beach at Baptist Health utilizes CBT throughout their programs. Unlike many other approaches, CBT has a short duration and high recovery rates. Whether it is your first time seeking care, or you are seeking help after a setback or during a time where you need additional support, it is possible to find cognitive behavioral therapy in your area.
If you or a loved one is seeking treatment for a substance use disorder, call The Recovery Village Palm Beach at Baptist Health to learn more about programs offered utilizing CBT. Patients at The Recovery Village Palm Beach at Baptist Health are given the tools needed to recover from substance use and co-occurring disorders.